Ideas & Solutions
Metal Circuit Boards
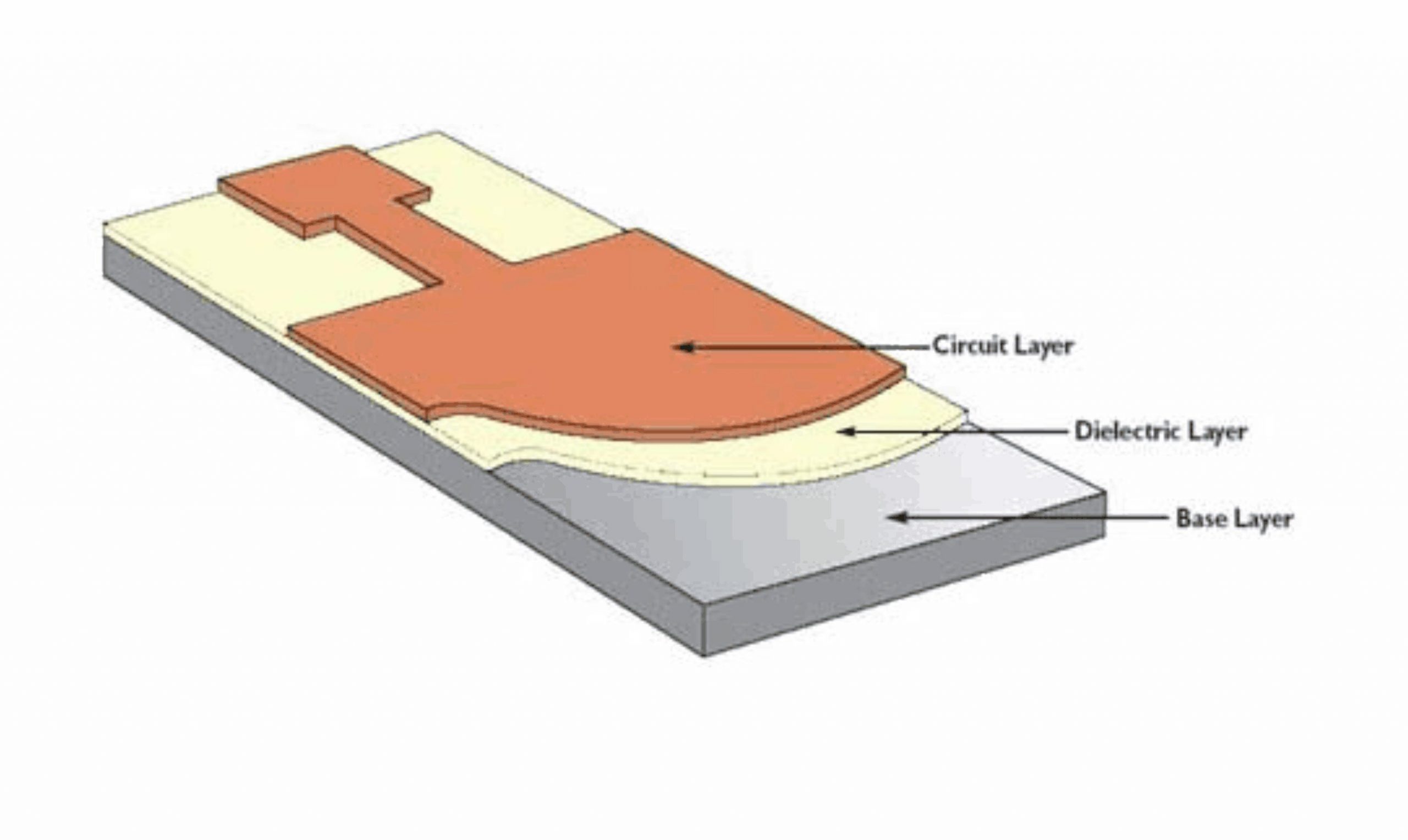
Electrically insulated metal substrates offer a low cost alternative to ceramic boards. Metal substrate circuitry consists of a metal base plate onto which a copper conductor layer is attached with a thermally conductive epoxy dielectric (see picture below, 2).
 In addition to aluminium, metal substrates such as copper, copper-clad Invar and copper-clad molybdenum are suitable as substrates (1). An aluminium alloy is usually chosen for the base metal for its excellent heat dissipation ability (see table below), mechanical integrity, low cost and lightweight construction.
In addition to aluminium, metal substrates such as copper, copper-clad Invar and copper-clad molybdenum are suitable as substrates (1). An aluminium alloy is usually chosen for the base metal for its excellent heat dissipation ability (see table below), mechanical integrity, low cost and lightweight construction.
 In addition to aluminium, metal substrates such as copper, copper-clad Invar and copper-clad molybdenum are suitable as substrates (1). An aluminium alloy is usually chosen for the base metal for its excellent heat dissipation ability (see table below), mechanical integrity, low cost and lightweight construction.
In addition to aluminium, metal substrates such as copper, copper-clad Invar and copper-clad molybdenum are suitable as substrates (1). An aluminium alloy is usually chosen for the base metal for its excellent heat dissipation ability (see table below), mechanical integrity, low cost and lightweight construction.
Thermal Conductivity and Thermal Expansion of different PCB Metal base plates (2)
| METAL/ALLOY | THERMAL CONDUCTIVITY (W/m-K) | COEFFICIENT OF THERMAL EXPANSION (ppm/K) |
| Copper | 400 | 17 |
| Aluminum | 150 | 25 |
| 304 Stainless Steel | 16 | 16.3 |
| Cold Rolled Steel | 50 | 12.5 |
| Iron | 80 | 11.8 |
| CIC Copper - Invar - Copper | 20 | 5.2 |
| CMC Copper - Molly - Copper | 200 | 6.5 |
| 20% ALSIC/Aluminum | 175 | 15 |
Design Considerations When Selecting the Base Metal Layer
- Coefficient Of Thermal Expansion And Heat Spreading
- Coefficient Of Thermal Expansion And Solder Joints
- Strength, Rigidity And Weight
- Electrical Connections To / Through the Base Layer
- Surface Finish
- Costs
References
- 1. Multilayer circuitry on metal substrates. Goran Matijasevic, Ormet Corporation, Carlsbad, CA.
- 2. Thermal Substrates: base. Comprehensive selection guide

