Ideas & Solutions
The Insulated Metal Printed Circuit Board
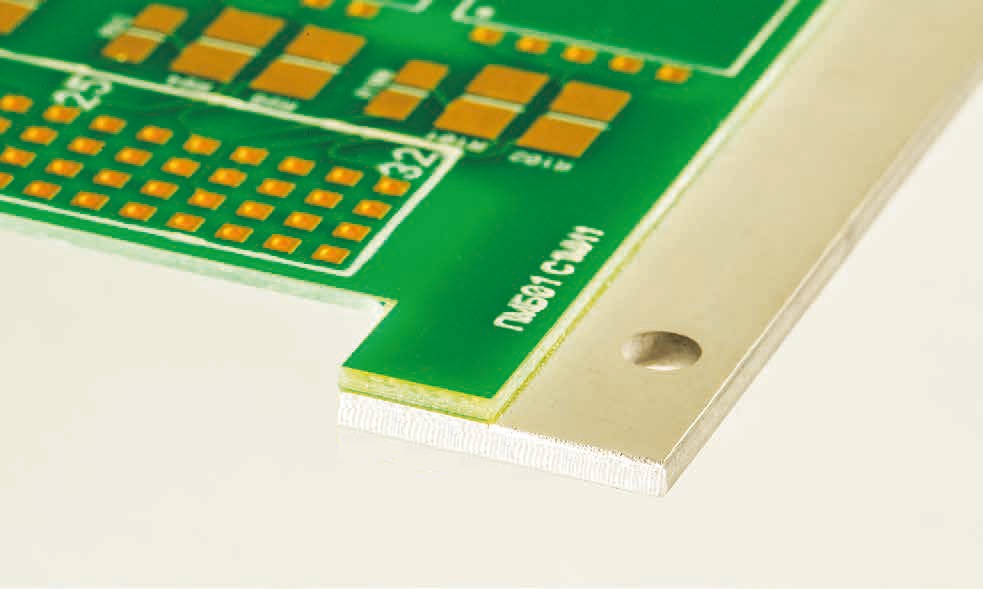
The Insulated Metal Printed Circuit Board (IMpcb) can replace Standard FR4 Boards or
Ceramic Substrates in Power or Thermal applications. The basic construction IMpcb is a
dielectric layer (2), between copper foil tracks (1) and a metal base plate (3).
 The primary technology is in the dielectric material, which must provide good thermal
conductivity and good dielectric isolation. Power Electronic Products today are being
required to provide more performance, in less space, and at lower costs. As a result,
the PCB or substrate must provide improved electrical, thermal and mechanical
performance. To meet these needs, designers must have the same electrical, thermal and
mechanical information, which would be expected with any electrical component. The
material manufacturers provide this type of information in Data Sheets, Design
Guidelines and Computer Models. The information allows the designer to plan and optimize
for performance, reliability, manufacturability and low cost. The IMpcb typically
simplifies the system architecture, resulting in performance, size, reliability and cost
advantages, which extend beyond the substrate or board. For instance
here you can find the Thermal Clad selection guide (10 Mb) of Co. Bergquist.
The primary technology is in the dielectric material, which must provide good thermal
conductivity and good dielectric isolation. Power Electronic Products today are being
required to provide more performance, in less space, and at lower costs. As a result,
the PCB or substrate must provide improved electrical, thermal and mechanical
performance. To meet these needs, designers must have the same electrical, thermal and
mechanical information, which would be expected with any electrical component. The
material manufacturers provide this type of information in Data Sheets, Design
Guidelines and Computer Models. The information allows the designer to plan and optimize
for performance, reliability, manufacturability and low cost. The IMpcb typically
simplifies the system architecture, resulting in performance, size, reliability and cost
advantages, which extend beyond the substrate or board. For instance
here you can find the Thermal Clad selection guide (10 Mb) of Co. Bergquist.
 Also Co. Thermagon has issued some usefull for all manufacturers, PCB designers and
end-users documents:
Also Co. Thermagon has issued some usefull for all manufacturers, PCB designers and
end-users documents:
 The primary technology is in the dielectric material, which must provide good thermal
conductivity and good dielectric isolation. Power Electronic Products today are being
required to provide more performance, in less space, and at lower costs. As a result,
the PCB or substrate must provide improved electrical, thermal and mechanical
performance. To meet these needs, designers must have the same electrical, thermal and
mechanical information, which would be expected with any electrical component. The
material manufacturers provide this type of information in Data Sheets, Design
Guidelines and Computer Models. The information allows the designer to plan and optimize
for performance, reliability, manufacturability and low cost. The IMpcb typically
simplifies the system architecture, resulting in performance, size, reliability and cost
advantages, which extend beyond the substrate or board. For instance
here you can find the Thermal Clad selection guide (10 Mb) of Co. Bergquist.
The primary technology is in the dielectric material, which must provide good thermal
conductivity and good dielectric isolation. Power Electronic Products today are being
required to provide more performance, in less space, and at lower costs. As a result,
the PCB or substrate must provide improved electrical, thermal and mechanical
performance. To meet these needs, designers must have the same electrical, thermal and
mechanical information, which would be expected with any electrical component. The
material manufacturers provide this type of information in Data Sheets, Design
Guidelines and Computer Models. The information allows the designer to plan and optimize
for performance, reliability, manufacturability and low cost. The IMpcb typically
simplifies the system architecture, resulting in performance, size, reliability and cost
advantages, which extend beyond the substrate or board. For instance
here you can find the Thermal Clad selection guide (10 Mb) of Co. Bergquist.
 Also Co. Thermagon has issued some usefull for all manufacturers, PCB designers and
end-users documents:
Also Co. Thermagon has issued some usefull for all manufacturers, PCB designers and
end-users documents:
-
Design Guidelines for Performance
- Thermal Properties
- Thermal Conductivity of the T-preg
- Thermal Resistance of the IMpcb
- Thermal and Power Management
- Dielectric Isolation
- Hipot Testing
- Dielectric Strength
- Reliability and Operation Life
- Foil Resistivity
- Maximum Copper Foil Current
- Capacitance
- Inductance
- Electrical Vias between Foil Layers
- Maximum Via Current
- Via Resistance
- Thermal Vias Application
- Thermal resistance of Via Pads
- General Thermal Via Considerations
- Thermal Vias in Applications without Base Plates
- Thermal Properties
-
Guidelines for Manufacturability with Thermagon IMpcb
- Basic Architecture
- Single Sided T-lam with Base Plate
- Double Sided Layer T-lam
- Multilayer T-lam IMpcb
- Multilayer IMpcb Hybrid with T-preg and FR4
- Base Plate
- Aluminum and Copper Alloys for Stamping, V-Scoring and Routing
- Properties of Aluminum and Copper Base Plates
- Special Base Plate Materials
- Anodized Aluminum Base Plates
- Singulation by Stamping, V-Scoring and Routing
- Substrate Camber and Flatness
- Panelization and Substrate Tolerances
- Substrate Radius, Holes, Bridges and Base Plate Ground Connections
- Dielectric Layer
- General Considerations
- T-preg, Thermal Dielectric
- FR4 and Special Dielectrics
- Copper Foil
- Material Selection and Properties
- Line and Space Considerations for Manufacturability
- Line and Space Considerations for Performance and Safety
- Plating, Solder and Special Coatings
- Electrical & Thermal Vias
- Via Size, Pitch and Plating
- Electrical Connections
- Thermal Enhancement
- Component, Mechanical Hardware and Mounting
- Component Considerations
- Mechanical Hardware and Mounting Issues
- T-lam Board and Substrate Mounting Issues
- Inspection & Test
- Electrical Inspection
- Mechanical Inspection
- Visual Inspection
- Procurement and Ordering
- Part Number System
- Typical Procurement Specification
- Assembly Guidelines
- SMD Assemblies
- Chip & Wire Assemblies
- Mechanical Assemblies
- Coatings, Encapsulations and Potting
- Special Applications More details about T-guide for Manufacturability with Thermagon IMpcb you can find here .
- Basic Architecture
-
Single Layered IMpcb Fabrication Guidelines you can find here .
-
Double sided and Multilayer Mpcb Fabrication Guidelines you can find here .

